
Last week a local legend passed away at the ripe old age of 95. A former NASA engineer who played a key role in developing the technology and mission strategy for the Apollo moon landing missions, John C. Houbolt was one of Joliet’s favorite sons — an Iowa-born farm boy who grew up working the land west of Joliet when it was a much smaller city than today; attended Joliet Junior College and the University of Illinois to become a civil engineer; and bucked the NASA bureaucracy in the early ’60s when he knew he possessed a superior approach for the incredibly difficult task of landing a manned spacecraft on the moon.
Houbolt’s A.P. obituary ran in the Joliet Herald-News last week, along with this feature article; yesterday (27 April 2014) the NY Times ran this excellent obituary, which is reprinted below. The Joliet Area Historical Museum in downtown Joliet features an outstanding exhibit on Houbolt’s work and legacy, The Soaring Achievements of John C. Houbolt.

On May 25, 1961, President John F. Kennedy told Congress that the United States should commit to landing a man on the moon before the end of the decade.
The goal caught some top officials at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration off guard. There was no firm plan for carrying out such a mission. Should they blast straight from Earth in a mammoth rocket? Should they launch a spacecraft into orbit around Earth, then deploy a module to travel from there to the moon?
Debate was intense. The celebrated NASA rocket scientist Wernher von Braun supported the big blast — an idea known as Nova. Others liked the Earth-orbiting option. For both, costs and complications seemed overwhelming.
Then a relatively obscure NASA engineer named John C. Houbolt committed a bold act of insubordination. In November of 1961, in a clear breach of protocol, Dr. Houbolt, a self-described “voice in the wilderness” whose ideas had been rejected by von Braun and others, wrote directly to Robert C. Seamans Jr., the associate administrator of NASA.
“Do we want to go to the moon or not?” asked Dr. Houbolt.
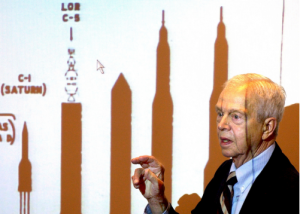
Since the 1950s, Dr. Houbolt, who was 95 when he died on April 15 in Scarborough, Me., had been arguing for a smaller, lighter and less expensive option — a Chevrolet, not a Cadillac, he liked to say — that was called lunar orbit rendezvous. According to this method, a rocket launched from Earth would send a spacecraft into orbit around the moon that would then deploy another vehicle, known as a “bug” or lunar module, to the lunar surface.
The module would carry two men who, after exploring the moon, would travel in the module back to the orbiting spacecraft and then return to Earth. It, too, was complicated, but it did not require the kind of massive rocketry the other approaches did — technology that did not yet exist.
“Why is Nova, with its ponderous ideas, whether in size, manufacturing, erection, site location, etc., simply just accepted, and why is a much less grandiose scheme involving rendezvous ostracized or put on the defensive?” Dr. Houbolt wrote to Dr. Seamans. “I fully realize that contacting you in this manner is somewhat unorthodox, but the issues at stake are crucial enough to us all that an unusual course is warranted.”
Until then, lunar orbit rendezvous had been dismissed as far-fetched. In 1961, no American had even orbited Earth — John Glenn would do so the next year — and there were broad concerns that the proposed sequence of events posed too many risks. It required multiple vehicles and complicated maneuvers high above the moon’s surface.
“Do not be afraid of this,” Dr. Houbolt urged Dr. Seamans, assuring him that he was not “dealing with a crank.”
Dr. Seamans surprised Dr. Houbolt by listening — and he made sure others at NASA did, too. In early 1962, Joseph F. Shea, a newcomer working as a top assistant to Brainerd Holmes, the head of manned spaceflight at NASA, began looking closely at Dr. Houbolt’s arguments. Dr. Shea soon became an advocate as well. In time, even von Braun came around, and in July 1962 NASA formally adopted lunar orbit rendezvous as its preferred method.
Seven years later, on July 20, 1969, the United States became the first and so far only country to put men on the moon. Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins deftly carried out the lunar orbit rendezvous. Armstrong and Aldrin entered the lunar module from the main spacecraft through a hatch so that they could travel the rest of the way to the moon — and back.
“Houston,” Armstrong said as the module landed on the lunar surface, “Tranquility Base here. The Eagle has landed.”
John Cornelius Houbolt was born on April 10, 1919, in Altoona, Iowa, and grew up in Joliet, Ill. His parents were farmers who had emigrated from the Netherlands. He attended Joliet Junior College before transferring to what is now the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, where he received a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering in 1940 and a master’s in the same subject in 1942. In 1958, while at NASA, he received a doctorate in technical sciences from ETH Zurich, in Switzerland.
He died of complications of Parkinson’s disease, his son-in-law P. Tucker Withington said.
Dr. Houbolt is survived by his wife of 65 years, the former Mary Morris; three daughters, Neil Withington, Joanna Hayes and Julie Winter; a sister, Irene Coonan; and four grandchildren.
In 1942, Dr. Houbolt joined NASA, then called NACA, for the National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics, as an engineer in the structures research division. He went on to hold numerous positions, including chief of the theoretical mechanics division. In 1963, after the lunar orbit rendezvous was adopted, he left NASA to become a senior executive with Aeronautical Research Associates of Princeton Inc.
He returned to NASA in 1976 as chief aeronautical scientist, retiring in 1985.
Although Dr. Houbolt was not at NASA in 1969, he was invited to witness the moon landing with other agency officials at Mission Control in Houston.
“John,” von Braun told him, “it worked beautifully.”