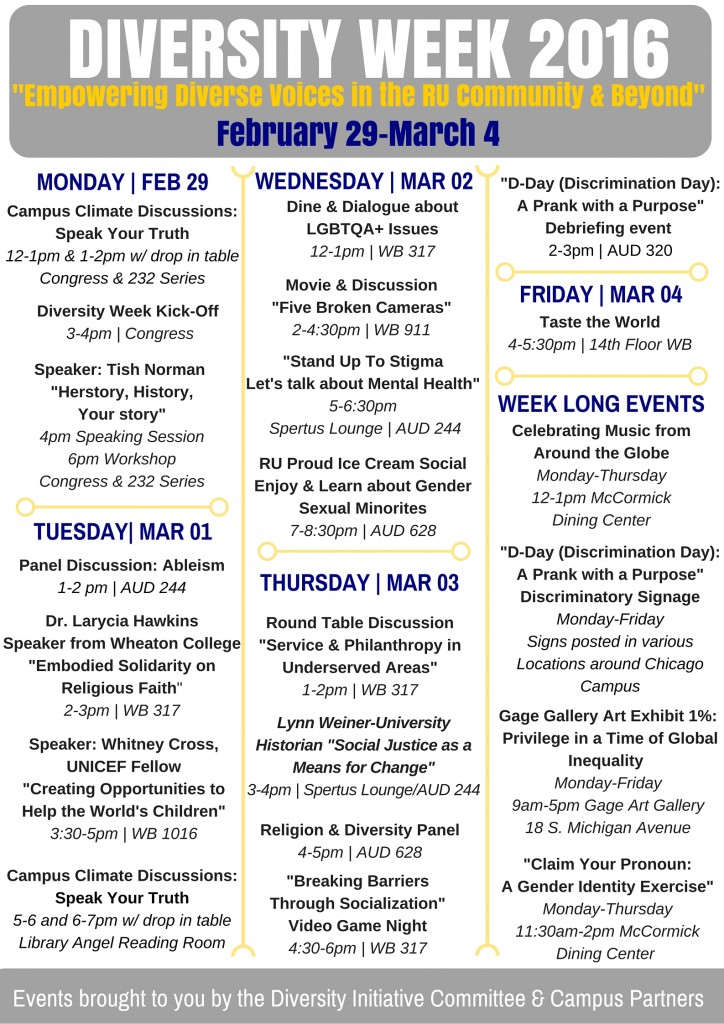
Category: Social justice
Two Canadian Filmmakers Drop by for an Interview

This past Sunday, Toronto-based independent filmmakers Geoff Norris and Kyle Lennan came by my house in Joliet to interview me about the long-simmering Peotone Airport controversy in agricultural lands south of Chicago in Will County, IL. Norris and Lennan have been making a film about the proposed Pickering Airport project in the rural areas near Toronto, which has resulted in the government seizure of property and demolition of homes over the past several decades despite no tangible progress on the airport’s construction.
The story bears an eerie resemblance to that playing out in eastern Will County within the vast stretches of prime Illinois farmland near the rural villages of Peotone, Monee, and Beecher. Geoff and Kyle came across my op-ed series about the Peotone airport written for the Joliet Herald-News up through 2012, and were kind enough to include me as a local voice from the community on their road trip to the Chicago area, where they also filmed local activists/opponents to the project.
SUST 350 Course Preview for Fall 2015

This coming fall semester (2015) I will be offering a transformational service learning course, SUST 350 Service and Sustainability, at the Chicago Campus. Our course theme is Urban Farming, Environmental Education, Community Development, & Social Justice.
- Title/number: SUST 350 Service and Sustainability (section 01)
- Semester offered: Fall 2015
- Location: Chicago Campus / Eden Place Nature Center
- Day/time: Tues 12-3pm
- Pre-req: UWR
SUST majors and minors may take this class to fulfill an upper-level SUST requirement, but 350 also is open to students at large who need a general education course or desire elective credit.
Introduction to the Course
SUST 350 focuses on one of sustainability’s “Three Es” — social Equity — within the broad context of Environmental stewardship and Economic development. Students will learn about one of the most important components of sustainability — food production and consumption — in the context of urban neighborhoods and ecosystems.
By doing hands-in-the-dirt labor at Eden Place Nature Center on the city’s South Side neighborhood of Fuller Park, students will gain direct knowledge of contemporary organic/urban agricultural systems as well as learn about pressing urban social justice issues such as food deserts, gentrification, pollution, environmental racism, and persistent poverty. The initial class meeting will be at RU’s Chicago Campus, and subsequent class meetings will take place at Eden Place Nature Center.

An urban farm is about food, but so much more besides. The Fuller Park community is an economically stressed neighborhood that is bisected by the Dan Ryan expressway and bounded by railroads on its eastern and western borders. Here, an urban farm and community nature center is a source of freshly grown, organic produce; a training ground for local youth in need of practical job skills; a stop valve in the Cradle-to-Prison pipeline; a gathering place for people of all ages in the community for physical exercise, informal education, and social events; a demonstration site for sustainable agricultural and ecological restoration techniques; a model of economic development on a local, sustainable scale; and a means of reconnecting urban folk to the natural world. More generally, in urban areas starved for jobs, green space, safe outdoor gathering places, and fresh quality food, enterprises like Eden Place productively and powerfully address the need for social equity and progressive change.

Our main focus will be on helping with various urban agriculture and environmental restoration projects at Eden Place Nature Center at 4417 S. Stewart, as well as at the Eden Place Farm at 4911 S. Shields. Our typical day will consist of meeting at the WB Lobby ~11:30am to take the Red Line to EPNC (students have the option of commuting there directly to meet at noon); convening at 12pm for discussion of assigned readings and, later in the semester, informal student presentations; and then working with Eden Place staff on various environmental, farm, and/or public education projects according to the needs and schedule of Eden Place.

The vast majority of our work takes place outside, regardless of weather. We built trails, planted trees, pulled weeks, raked leaves, managed compost piles, helped set up activities and structures for Octoberfest, repaired and installed fences, and many other chores/activities. We also interacted with EPNC staff to learn about their mission and vision for the future. Last but not least, we always had a little time each week to visit with EPNC’s many animals, including Gaga the goat (who loved to intervene during our roundtable discussions in the gazebo!).
Partner Organization: Eden Place Nature Center
From the Eden Place website:

“In 1997, community member, founder, and Executive Director of Fuller Park Community Development Michael Howard [pictured at left] was concerned about the serious lead poisoning problems affecting the neighborhood children. Through research he discovered that Fuller Park contained the highest lead levels in the city of Chicago. As a community leader he wanted to make some serious changes for the sake of his family and his entire neighborhood, and he decided that this work would start with the illegal dumpsite located across the street from his home.
“Mounds of waste over two stories tall encompassed the entire three acres of land. Mr. Howard acquired the deed for the land and involved the community in a large scale, three year clean-up of the dumpsite. Alongside his wife and fellow activist Amelia, and in partnership with hundreds of volunteers and community members, Mr. Howard led a clean-up project in which more than 200 tons of waste including concrete, wood, tires and other toxin-laced materials were removed from the site.

“Upon clean-up of the site, the next step was development. Tons of fresh soil were brought in to establish the Great Lawn, and the Hope Mound was established as the first permanent fixture on Eden Place. South Point Academy trainees contributed a number of early structures to the Eden Place grounds, including the gazebo, DuSable Trading Post, and the storage sheds. The Mighty Oak and other surrounding trees formed the woodland at the north end of the property, including a reflecting pond meant to encourage reflection and respite from the urban surroundings.
“In May of 2004, Eden Place was honored by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Chicago Wilderness with The Conservation and Native Landscaping Award. The winners were recognized for their extensive and creative use of natural landscaping to support native plants and animals that contribute to the region’s biodiversity. That same month, Eden Place was filmed for a PBS special documentary called Edens Lost & Found. This documentary profiles activists and organizations in Los Angeles, Seattle, Philadelphia, and Chicago who are attempting to ‘improve the quality of life and public health by encouraging community and civic engagement through the restoration of their urban ecosystems.’

“Eden Place has continued to develop and grow with the support and recognition of local leaders and organizations. We have worked to raise awareness amongst community members about the environmental problems that have affected their families for years. Local residents are making connections with nature like never before, and they are feeling a sense of community pride like never before. However, our work in the community is not finished. More than 3/5 of the local area is comprised of abandoned lots where homes and various industries once thrived, and Fuller Park residents still carry the burden of one of the highest local lead contents in the city. Through our partnership with local and national conservation organizations such as the Chicago Zoological Society, the Audubon Society, the U.S. Forest Service International Programs, Chicago Wilderness, Openlands, and NeighborSpace, we will continue to establish green community space and education that will improve the health and well-being of our community.”
For more information on this unique service learning course, please contact Prof. Mike Bryson (mbryson@roosevelt.edu or 312-281-3148).
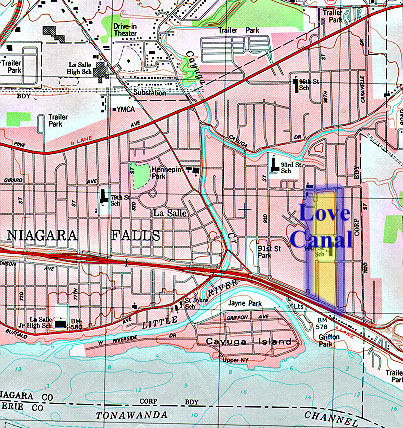
Love Canal: a Still Unfolding Legacy of a Toxic Waste Community Disaster
 This week the New York Times features a “retro report” on Love Canal, one of the most infamous environmental disasters in US history and the incident that spurred the creation of the EPA’s Superfund program.
This week the New York Times features a “retro report” on Love Canal, one of the most infamous environmental disasters in US history and the incident that spurred the creation of the EPA’s Superfund program.
Far from a closed book, the legacy and implications of Love Canal are still playing out. Of great significance in the history of the American environmental justice movement, Love Canal also demonstrates the difficulty and complexity involved in scientifically assessing the health impacts of environmental toxins on a relatively small population.
The above map is one of the many images collected in the online resource, Lessons of Love Canal, developed in 2003 by the Boston University School of Public Health. As noted in the site’s introduction:
Many community groups around the U.S. request health studies to examine associations between environmental contamination and perceived health problems. Love Canal and other community battles have taught us that how studies are conducted and by whom is crucial to deriving useful and credible information. At the Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH), we push for community concerns and insights to be part of the study process from the beginning to the end.
Some Love Canal studies have become models for the way we do community environmental health studies today. We hope this collection of lessons learned over three decades of controversy at Love Canal represents initial steps toward building a resource for future community-based studies.
IL EPA Hears Southeast Side Residents’ Complaints about Petcoke Piles along Calumet River
Last Thursday the Illinois EPA held a contentious public meeting on Chicago’s SE Side to hear residents’ concerns and complaints about the massive piles of petcoke — a waste by-product of tar sands oil refining done in nearby Whiting, IN — being accumulated along the industrialized banks of the Calumet River, in close proximity to the East Side and Deering neighborhoods of Chicago.
As reported here last Friday, 15 Nov 2013, by Progress Illinois:
A Chicago community meeting the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (IEPA) hosted to discuss a proposed construction permit for KCBX Terminals Company quickly escalated into angry shouting from Southeast Side residents fed up with the firm storing large piles of petroleum coke, or petcoke, near their homes.
KCBX, which is controlled by the conservative billionaire brothers Charles and David Koch, stockpiles the petcoke, a byproduct of oil refining, along the Calumet River on Chicago’s far Southeast side. The thick, powdery petcoke is sent to KCBX from a BP refinery in Whiting, Indiana. East Side and South Deering residents have been sounding the alarm for some time now that petcoke dust is blowing into their neighborhoods and getting into their homes.
“No one asked us if we wanted to have these piles dumped in the first place. They just did it,” Southeast Side resident Sue Garza told the IEPA officials at the packed two-hour meeting, held at the East Side United Methodist Church. “We have been the toxic dumping ground here for over 100 years. We don’t want it anymore.”
Brad Frost with IEPA’s office of community relations said KCBX is seeking a revised construction permit from the agency in order to bring new equipment, including 10 portable conveyors, a stacking conveyor and a portable hopper, to its site at 10730 S. Burley Ave. According to Frost, the company is not looking to increase its input or emissions.
“They can’t handle their [petcoke] dust now,” resident Guillermo Rodriguez fired back. “How is it not going to increase?”
Residents grew frustrated with IEPA officials, pointing out that the community is against the company’s activities and noted that issuing such a permit would allow for its site expansion.
“It is very simple,” said community member Martin Morales. “We don’t like it. We don’t want it. (Petcoke pollution is) making us sick. What else do you need?”
One person later shouted, “Move the piles! Who cares about the conveyors?” Another said, “If you’re the protection agency, protect us!”
“How many people have to get sick before you do something,” asked resident Ken Keefer. “Is there a certain number that have to come down with asthma or cancer before you do something? This has been going on for two, three years. And this is the first time you guys have shown up.”
Frost said the IEPA would take into account the comments made at the meeting, but noted that the IEPA has received very few formal, written complaints about specific issues involving the site.
One man fired back, “We can’t even open our windows because of the soot.” Later, the audience began to chant, “Move the piles!”
“Answer the question. When are you going to move the piles,” a gentleman asked the officials, which promoted another person to exclaim, “When we’re all dead!”
“Obviously there a lot of people here concerned about the facility,” Frost stressed. “We need to see [formal] complaints. That’s one thing we use to determine whether there are problems at sites.”
Frost did make a point, however, to stress that even though the agency has received few formal complaints, the IEPA is pursing enforcement against the company.
Earlier this month, Illinois Attorney General Lisa Madigan filed a lawsuit on behalf of IEPA against KCBX over alleged air pollution violations. In a statement, Madigan said the toxic mounds at KCBX’s storage site “are growing by the day without the appropriate protections to ensure nearby residents’ health and safety.”

Community members asked lawyers from the attorney general’s office, who attended the meeting, what else could be done to more quickly shut down the facilities and get rid of the petcoke mounds. The officials stressed that the current case is pending, and it has to go through a formal legal process.
Additionally, a group of Southeast Side families filed a lawsuit at the end of October against KCBX and a few other companies that store petcoke. The lawsuit came on the heels of notices of air pollution violations the IEPA recently issued to Beemsterboer Slag Co., which also stockpiles the coal-like waste product along the Calumet River.
BP is in the process of modernizing its Whiting refinery and plans to to boost the amount of petcoke it produces at the facility to 2.2 million tons of a year.
Tom Shepherd with the Southeast Environmental Task Force told the crowd that the current issues the community is experiencing is only “the tip of the iceberg.”
“There’s going to be at least three times more than is over there today,” he said. “Today we’re getting 700,000 tons a year, but once that coker goes online, it’s going to increase to 2 million tons a year. That’s 6,000 tons a day.”
“Imagine how many trucks, barges and trainloads are going to be coming through our neighborhood,” Shepherd continued. “If they’re getting a permit for 10 additional conveyors over there, that means that they’re going to increase ten-fold, but we heard three-fold. That’s scary enough.”
The audience really got peeved when they learned the IEPA has to make a decision regarding KCBX’s permit next week. IEPA officials wouldn’t say whether they would be extending the review period for the permit, approving the permit or denying it.
“You’re here a week before,” Rodriguez later asked. “Where were you when this all started, when this began? Where were you then? Who’s protecting our water source? They’re pumping water out of that lake and they’re spraying their piles. That runoff goes where? It goes into our streets. It goes into our drinking water. If you think this is a good idea, let’s put it in your backyard.”
Residents called on Ald. John Pope (10th), who attended the meeting, to speak, but then heckled and interrupted him. Pope made a point to stress that he has been working with elected officials at the local, state and federal levels to see what can else be done about the piles.
“As much as we all are passionate about the problems, there’s got to be a formal process, and it starts unfortunately with the complaints,” he added. “I know everyone’s complained in the past, but there’s got to be formal complaints lodged.”
Piles and Piles of Petcoke: Environmental Justice along the Calumet River
 Today’s Mike Nowak Show on WCPT features a segment about the petcoke controversy in the Calumet Region of Chicago’s far South Side. This waste by-product from the refining of oil from the tar sands of Canada has been piling up along the banks of the Calumet River by Koch Industries, on behalf of BP, which operates a refinery across the state line in Whiting, IN. As noted below, the piles give off clouds of dust in windy conditions, which then disperse among the adjacent neighborhoods — communities that have endured decades of environmental hazards and industrial degradations from steel plants, fuel refineries, landfills, and illegal waste dumps.
Today’s Mike Nowak Show on WCPT features a segment about the petcoke controversy in the Calumet Region of Chicago’s far South Side. This waste by-product from the refining of oil from the tar sands of Canada has been piling up along the banks of the Calumet River by Koch Industries, on behalf of BP, which operates a refinery across the state line in Whiting, IN. As noted below, the piles give off clouds of dust in windy conditions, which then disperse among the adjacent neighborhoods — communities that have endured decades of environmental hazards and industrial degradations from steel plants, fuel refineries, landfills, and illegal waste dumps.
I’m reproducing Nowak’s written preview of his radio show here, because (just as he does for his radio show every week) it maps out many of the twists and turns of this emerging storyline, plus provides numerous links to news and environmental resources.
Pet coke piles along the Calumet River: Did they come from Detroit?
Ten days ago I received this message from Tom Shepherd of the Southeast Environmental Task Force (SETF):
Dear Friends in the Clean Power Coalition and All Others,
Thank you to those in the coalition and others that have joined the Southeast Environmental Task Force in coming to the table to try to find a solution to the petcoke problem that has been developing on the southeast side. The petcoke is a by-product (or waste product, if you will) of the tar sands that are being pipelined and shipped in other ways to the British Petroleum refinery in Whiting, Indiana (just over the state line from Chicago) for processing.
Much has happened in the weeks since we met to discuss this urgent problem:
We have conducted two tours for legislators and staffers of public officials; met with Koch Bros. / KCBX company officials; have been out on the Calumet River twice doing inspections and video shoots; given a host of interviews; have been fielding numerous calls and complaints; prompted investigations by the USEPA and Illinois Atty. General; and are planning a community meeting on Oct. 24 to raise awareness and to educate neighbors nearest to the huge, black piles of dusty petcoke that are most affected by it.
You would think that a part of Chicago that has suffered so much environmental degradation would at some point catch a break.
You would be wrong.
With the shuttering of three coal fired power plants in the area–the State Line, along the border of Illinois and Indiana, as well as the Fisk and Crawford plants in Chicago–the need for coal and accompanying storage facilties in which to keep it has dropped dramaticaly.

But in an almost perverse turn of events, the controversial BP Whiting, Indiana refinery is about to finish a $3.8 billion expansion, which will make it the world’s second largest coker, which will process Canadian tar sands at an astounding rate. One of the by-products of that industry is something called petroleum coke or “petcoke.” According to Henry Henderson at the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC),
BP Whiting is now the second biggest producer of petcoke amongst American refineries. They will be spitting out 6,000 tons of the stuff a day ; more than 2 million tons annually.
Unfortunately, petcoke has a nasty habit of becoming wind-borne and ending up on people’s counter tops, windsills and in their eyes and lungs. And BP is now moving vast amounts of this substance across the state line to Chicago to holding areas on the banks of the Calumet River. Why? Because the environmental regulations aren’t as strict here. Which is ironic, considering that just last year BP agreed to a $400 million settlement with state and federal agencies as well as environmental and community groups over air quality standards around the Whiting facility.
At least this time, the threat to Chicago’s southeast side is being reported by some of the local media, including the Chicago Tribune and Chicago Tonight on WTTW. After being alerted by SETF, NRDC produced its own video of the rising piles of petcoke along the Calumet.
And Chicago isn’t even the first city to deal with this particular issue. Earlier this year, citizens of Detroit were alerted to similar clouds of black soot wafting over communities along the Detroit River. After public outrage from neighborhood groups and online entities like Sw Detroit Marathon Exposed and DCATS – Detroit Coalition Against Tar Sands, Detroit Mayor Dave Bing ordered the piles removed.
But where did the stuff end up? Nobody seems to know.
That’s where the headline at the top of this story comes from. The SETF’s Tom Shepherd says that he has asked the companies storing the petcoke in Chicago exactly where it came from and how it got there so quickly. But he has not received a straight answer. Is it possible that Chicago is now storing the petcoke that was ordered out of Detroit?
How are these two cases similar and how do they differ? According to a story on Climate Progress,
Detroit’s pet coke piles were produced by Marathon Refinery but owned by Koch Carbon, a subsidiary of Koch Industries. In Chicago they are owned by KCBX, an affiliate of Koch Carbon, which has large parcels of land along the Calumet River and, according to Midwest Energy News, expanded its presence in the area last year.
As you can see, the common denominator is Koch Industries. From an article on Daily Kos:
Because it’s a waste product of oil refining the Kochs sell it for prices cheaper than coal to poor nations willing the accept pollution as a trade off for cheap energy. Petcoke is the carbon cost ignored in the State department analysis that falsely claimed that Keystone XL tar sands oil will not significantly increase greenhouse gas pollution compared with conventional oil.

Which leads some people to refer to the substance as “petkoch.” The other connections, as noted above, are issues like the transportation of tar sands oil, the Keystone XL Pipeline, and recent tar sands oil spills like the one near Kalamazoo, Michigan, in 2010. Three years later, tar balls can still be found along the banks of that river, and dozens of families have been permanently displace.
That led to an action by the Michiana Coalition Against Tar Sands (MICATS) in September. As reported, interestingly, in the eNews Park Forest, they
set up a blockade of Enbridge Inc.’s expansion of tar sands pipeline 6b. This pipe- the same that ruptured in 2010 causing the largest and costliest inland oil spill in history- is currently under construction to increase the flow of tar sands from 240,000 barrels per day to 500,000 barrels per day.
It never ends, does it.
To address this very serious environmental issue, I’m pleased to have Tom Shepherd from SETF in studio. Joining us via phone are Chris Wahmhoff of Michigan Coalition Against Tar Sands (MI CATS) and Stephen Boyle from DCATS. By the way, Boyle points out that the Calumet River is currently the subject of remediation efforts by the U.S. EPA:
The 1.8-mile stretch of the river from Indianapolis Boulevard to Hohman Avenue is currently undergoing projects designed to remove contaminants and restore habitat. 350,000 cubic yards of sediment are slated to be removed and a cap will be placed over the dredged sediment. Wetlands and nearshore habitats will be restored with native plants following the completion of the dredging, expected in 2016.
Gosh, I can’t imagine that tons and tons of petcoke could possible affect that planned restoration.
Source: Mike Nowak, “This Week’s Show” (27 Oct 2013)
CIMBY Students Visit RU Campus and Tour Stearns Quarry Park
Last month I had the great fortune of playing host at Roosevelt’s Chicago Campus to a terrific group of Chicago Public High School kids from the far South Side — the Calumet region, specifically — for a sustainability-themed tour of the university and a little bit of urban nature field-tripping.

These students are leaders within the noted Calumet Is My Back Yard environmental education program, in which dozens of high school teachers and hundreds of students participate in several ecological/community restoration projects on Chicago’s Far South Side — and in the process, learn about urban ecology, community development, and the history of this industrialized yet still biodiverse landscape. The 12-year-old program is a collaboration between the Field Museum of Natural History and Chicago Public Schools.
Our day started by meeting up at RU’s Wabash Building, then heading up to an 11th floor classroom that features spectacular views of the city’s lakefront. I conducted a simulated college class session on the topic, “Sustainability and Urban Nature: An Introduction to Roosevelt University and Exploration of the Chicago River” (pdf). There was no trouble getting discussion going with this group! We had such a good give-and-take during my talk that I could cover only half of my slides.

After this session, we enjoyed a student-led tour of the Wabash Building residence hall, fitness center, and other highlights — with a short stop at the Tutoring / Student Support center in the historic Auditorium Building. Then, a tasty lunch at the 2nd floor Dining Center, where I got to visit with several of the students as we munched our hot dish.
To cap off our day, we headed outside with work gloves and trash bags to hop the L and ride the Orange Line to Stearns Quarry, aka Palmisano Park — a relatively new urban parkland on the near SW Side in the Bridgeport neighborhood. A former limestone quarry until the 1970s, and then a landfill until the 2000s, Stearns Quarry Park is now a model of sustainable parkland development, and a great place to talk about land use, the relation between land and water, urban biodiversity, and the history of Chicago.

We hiked the park’s extensive trails, chatted and laughed, and collected litter and recycling along the way. I don’t know how many readers have had a chance to do that with boisterous and fun-loving high schoolers, but I can tell you that I thoroughly enjoyed it! The highlight of our visit was when we took in the view at the meadow on the hilltop, which offers great views of the downtown skyline as well as the Fisk Generating Station — a recently shuttered coal-fired power plant which for many decades spewed pollution here on the SW Side until environmental activists succeeded in pressuring Midwest Generation to shut it down.

Here, in the shadow of the Fisk plant, two CIMBY students told of the community service work they’ve been doing with key grassroots environmental organizations — the Southeast Environmental Task Force, which is based in Calumet; and the Little Village Environmental Justice Organization, here on the SW Side. These inner-city teens were passionate, articulate, and highly informed — and the impact of what they had to say in just a few minutes didn’t just complement my previous lecture about sustainability and social justice . . . it totally blew it away.
You can check out more photos of our day together here in this online album.

Action Research at the Chicago Lights Urban Farm

Many of the writing and research assignments I give my students at RU are fairly straightforward and prescriptive. I give them a lot of concrete guidelines and freedom to choose a topic; they crank out the work; and then I grade it and give it back with feedback. That’s how it works for the most part in academia.
But the past two springs I’ve had the privilege of teaching a service-learning course held on-site at the Chicago Lights Urban Farm, at the south end of the Cabrini-Green neighborhood on Chicago’s Near North Side — and that class is anything but ordinary.

SUST 350 Service & Sustainability has been supported these last two years by a “transformational service learning” grant from Roosevelt’s Mansfield Institute of Social Justice and Transformation, funding which has enabled my students and me to support the farm’s mission, purchase supplies for construction projects, and take area youth on educational field trips within and beyond Chicago.
This spring semester, in addition to their weekly work on the farm watering plants, building compost bins, turning over soil, constructing greenhouse grow tables, etc., my 15 undergrad students were tasked with a collaborative “Action Research” project, in which they’d work in pairs or trios to develop real-world projects meant to extend and enhance the mission and work of this extraordinary half-acre urban farm.
Having never led quite such a research project before, I wasn’t exactly sure how to instruct them in this process — consequently, I just didn’t have the procedure or the finished project all scripted out like I usually do. Instead, I offered some rough guidelines (see project guidelines here [pdf]), moral and logistical support (likewise provided by the farm’s director, Natasha Holbert), and a lot of room for creativity.
Boy, did I learn something. Give motivated, smart, and engaged students a chance to do creative applied research for a place that they respect and appreciate, and they are capable of doing terrific work. (Note to self: do this again.) Here’s what they came up with. All of these Action Research Projects are designed to be implemented, expanded, and/or revised by the Farm staff and workers — and some may be taken up and extended by future SUST 350 students here at Roosevelt.

Community Empowerment and Youth Enrichment (CEYE) Program
Allison Breeding, Scott Rogers, and Troy Withers
The CEYE Program is comprised of three branches—Community Service, Food Access and Engagement, and Roosevelt Credit—which collectively aim to benefit the lives and futures of Chicago Lights Urban Farm (CLUF) volunteers, at-risk urban youths, and Cabrini seniors. CEYE seeks to take teens out of a path of trouble and into a path of service, volunteerism, and eventually college and career. The program also seeks to empower and assist local seniors by improving their food access and strengthening their community connections. (CEYE Proposal pdf)
Community Gardeners’ Guide
Jordan Ewbank, Kristen Johnson, and Ana Molledo
A practical how-to resource for people wishing to start their own community garden, based on the knowledge and practices of the CLUF community garden, established in 2002. Discusses land preparation, garden organization and design, raised beds vs. in-ground gardening, soil quality, compost, and what kinds of vegetables to grow. (Gardeners’ Guide pdf)

Farm Education Lessons and Activities
Bob Basile, Christian Cameron, and Molly Connor
Educational lessons and activities for K through Grade 6 students on composting, planting, and nutrition meant to be used at the CLUF to connect urban farm education with sustainability. May be expanded by future students for 7-12 grade levels on these and additional topics. (Farm Curriculum pdf)
Knowing Your Neighborhood: Community Assets Brochure and Map
Mike Miller and Ken Schmidt
Brochure (pdf)and interactive Google map designed to highlight resources and assets with a one-mile radius of the Chicago Lights Urban Farm.
Rainwater Harvesting Plan
Michael Magdongon and Lore Mmutle
A concrete proposal for the installation of a rainwater harvesting system on one of the Farm’s hoop houses. Would provide a sustainable supply of water to decrease dependence upon usage of the street hydrant on Chicago Ave., now the Farm’s main water source. Projected return on investment within one year.
(Rainwater Proposal pdf)
Self-Guided Tour and Farm Map
Bryan McAlister and Lauren Winkler
This beautifully designed one-page, double-sided guided tour information sheet and map is ideal for first-time visitors to the Farm who would like a brief and fun introduction to all of the spaces and growing areas within its half-acre footprint. Includes information of selected vegetables and several recipes for cooking them.
(Guided Tour and Map Brochure pdf)
Joliet Shouldn’t Be a (For-Profit) Prison Kind of Town
As my family and I drove over the river to Joliet’s East Side, I had little idea what to expect at our Collins Street destination — a fundraiser by the local grassroots organization Concerned Citizens of Joliet. All we knew was that the gathering was for a good cause: raising awareness about and galvanizing community resistance to the prospect of a for-profit immigration detention center being built here in Joliet.

When we entered Azteca de Oro banquet and dance hall, though, I sensed instantly that it would be a memorable evening. Friendly greeters directed us to a comfortable table right next to the dance floor, which thrilled my two girls. A boisterous Mariachi band was in full voice from the stage at one end of the hall, while at the other end happy folks mingled and laughed at a well-stocked bar.
And the food! Long buffet tables full of stewed chicken, sautéed beef and vegetables, rice, refried beans, tortillas, salads, and sweet treats beckoned, and I’ll admit we weren’t shy about asking for seconds.
But the best part of the evening was the music and dancing, of which there was a glorious abundance. Musical acts of all stripes and colors entertained the swelling crowd, including the inspiring gospel of the Mt. Zion Tabernacle Choir, the witty folk/pop/rock stylings of singer-guitarist Dan Droogan, and the hot salsa of the Sangre Latina dance band.
This joyous music from musicians black, white, and brown filled the hall as dozens of children took to the dance floor to run, skip, chase each other, play hide and seek, and make new friends. Soon the hall’s lights came on in their full resplendence, and the adults joined the kids in what became one of the most festive scenes I’ve witnessed in a long time.

But the spoken word, both Spanish and English, was part of the program, too. Local politicians, including Will County Board members Reed Bible of Plainfield and Denise Winfrey of Joliet, and community organizers took the stage to decry the prospect of an immigrant prison here in Joliet. As I contemplated their message of critique and concern, I reflected on the irony of our location. Just a stone’s throw from us on Collins Street was Illinois’ ultimate penal icon: the Old Joliet Prison, decommissioned and deteriorating since 2002.
Yes, Joliet might someday make some money from its undeniably long prison legacy, though that civic identity has always been problematic for us. But not, I hope, through the construction of a for-profit immigrant “detention center” that is dedicated to the pocketbooks of its potential owners (in this case, Corrections Corporation of America) rather than the welfare of its detainees — most of whom will be our Hispanic brothers and sisters.
 Instead, we should look north from Azteca de Oro and do something productive with the Old Joliet Prison before its massive limestone walls crumble to the ground. Expensive, yes — but interpretive signs in the parking lot for Route 66 tourists don’t fill the tax coffers, either.
Instead, we should look north from Azteca de Oro and do something productive with the Old Joliet Prison before its massive limestone walls crumble to the ground. Expensive, yes — but interpretive signs in the parking lot for Route 66 tourists don’t fill the tax coffers, either.
No, folks — we don’t need another prison here. Certainly not one focused on pieces of silver rather than social justice. Joliet’s ongoing flirtation with such a prospect should be closely monitored and vociferously protested by all people of conscience.
A shorter version of this article on Sunday, 18 march 2013. Also see this 20 March 2013 op-ed piece, “Make Joliet a City of Jobs, Not Jails,” by Mark Meinster of Warehouse Workers of America.
A Personal Note to Midwest Generation
Dear Midwest Generation:
I admit it. For a long time I’ve assumed that you were nothing but a bureaucratic, ethics-challenged, profit-obsessed energy company. But your recent pleas to the Illinois Pollution Control Board for sympathy and understanding regarding your supposedly tardy efforts at environmental compliance have truly touched my heart.

After all, you’ve owned the coal-burning Joliet and Romeoville power stations since 1999, which practically feels like yesterday. That’s hardly time enough to implement industry standard pollution-control upgrades as dictated by the Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act, and other annoying environmental laws written by people overly fixated on sulfur dioxide emissions or airborne particulate matter.
Burning coal generates electricity for us, which we love, and quite a bit of money for you, which you need. Hey, power company executives gotta eat, too, don’t they? After all, electricity production isn’t a charity endeavor — that would be (gasp!) socialism.

But making a profit in your business is tough these days, what with your outdated and inefficient power plants in Will County spewing so many pollutants that require “scrubbing” and various “mitigations.” Some of your chief critics — like Citizens Against Ruining the Environment, the Sierra Club, and the Illinois Attorney General’s office — don’t get that. They just keep whining that your coal plants are old and dirty and unhealthy.
C’mon, already. A little dirt never hurt anyone, except maybe a few finicky armchair environmentalists. You don’t hear the tens of thousands of working class and minority citizens living downwind of your coal plants complaining, do you? And is it really such a big a deal that you haven’t figured out what to do with those toxic coal ash waste piles you’re adding to on a daily basis?
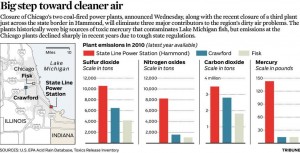 I would remind people that you did a pretty nice thing last year when you closed those two legitimately old coal-fired power plants on Chicago’s Southwest Side — the Fisk (built in 1903) and Crawford (1924) stations. For most of thirteen years after you bought them, you studiously ignored longstanding protests by neighborhood environmental watchdogs, ultra-liberal aldermen, and grandstanding green organizations. But once you finally determined that those old-timer plants weren’t going to turn a profit anymore if you installed their required upgrades, you quickly and decisively shut them down.
I would remind people that you did a pretty nice thing last year when you closed those two legitimately old coal-fired power plants on Chicago’s Southwest Side — the Fisk (built in 1903) and Crawford (1924) stations. For most of thirteen years after you bought them, you studiously ignored longstanding protests by neighborhood environmental watchdogs, ultra-liberal aldermen, and grandstanding green organizations. But once you finally determined that those old-timer plants weren’t going to turn a profit anymore if you installed their required upgrades, you quickly and decisively shut them down.
That was brave. So was letting all those Fisk and Crawford plant workers go. That’s why I’m sure that if and when the time comes to “release” the workers from your barely middle-aged Joliet station (which currently emits far more pollution than those old Fisk and Crawford plants combined), you’ll find a way to pull the trigger.
As for eventually complying with these new environmental regulations on sulfur dioxide? I’m grateful for your promise to get to it some year.
So shame on those ladies from CARE and those Sierra Club treehuggers and Pollution Board pencil pushers for badgering you with complaints, lawsuits, op-ed articles, scientific studies, mortality statistics, medical expense projections, probing questions, and other distractions. I wish they’d give a chronic and habitual polluter like you some credit for trying to reform itself. It’s obvious you’re trying, really trying.
Heck, by 2025 or so I’m sure you’ll have our Joliet smokestacks clean as a whistle.
I live in Joliet, about three miles as the smoke drifts from the Joliet 29 Generating Station on Route 6 operated by Midwest Generation since 1999. This is a revised version of my monthly op-ed column for the Joliet Herald-News. Check the Illinois Pollution Control Board’s website to learn how the regulatory process works and for information on Midwest Generation’s appeal for more compliance time as well as other pending issues.