Today’s Mike Nowak Show on WCPT features a segment about the petcoke controversy in the Calumet Region of Chicago’s far South Side. This waste by-product from the refining of oil from the tar sands of Canada has been piling up along the banks of the Calumet River by Koch Industries, on behalf of BP, which operates a refinery across the state line in Whiting, IN. As noted below, the piles give off clouds of dust in windy conditions, which then disperse among the adjacent neighborhoods — communities that have endured decades of environmental hazards and industrial degradations from steel plants, fuel refineries, landfills, and illegal waste dumps.
Today’s Mike Nowak Show on WCPT features a segment about the petcoke controversy in the Calumet Region of Chicago’s far South Side. This waste by-product from the refining of oil from the tar sands of Canada has been piling up along the banks of the Calumet River by Koch Industries, on behalf of BP, which operates a refinery across the state line in Whiting, IN. As noted below, the piles give off clouds of dust in windy conditions, which then disperse among the adjacent neighborhoods — communities that have endured decades of environmental hazards and industrial degradations from steel plants, fuel refineries, landfills, and illegal waste dumps.
I’m reproducing Nowak’s written preview of his radio show here, because (just as he does for his radio show every week) it maps out many of the twists and turns of this emerging storyline, plus provides numerous links to news and environmental resources.
Pet coke piles along the Calumet River: Did they come from Detroit?
Ten days ago I received this message from Tom Shepherd of the Southeast Environmental Task Force (SETF):
Dear Friends in the Clean Power Coalition and All Others,
Thank you to those in the coalition and others that have joined the Southeast Environmental Task Force in coming to the table to try to find a solution to the petcoke problem that has been developing on the southeast side. The petcoke is a by-product (or waste product, if you will) of the tar sands that are being pipelined and shipped in other ways to the British Petroleum refinery in Whiting, Indiana (just over the state line from Chicago) for processing.
Much has happened in the weeks since we met to discuss this urgent problem:
We have conducted two tours for legislators and staffers of public officials; met with Koch Bros. / KCBX company officials; have been out on the Calumet River twice doing inspections and video shoots; given a host of interviews; have been fielding numerous calls and complaints; prompted investigations by the USEPA and Illinois Atty. General; and are planning a community meeting on Oct. 24 to raise awareness and to educate neighbors nearest to the huge, black piles of dusty petcoke that are most affected by it.
You would think that a part of Chicago that has suffered so much environmental degradation would at some point catch a break.
You would be wrong.
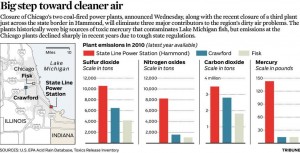
With the shuttering of three coal fired power plants in the area–the State Line, along the border of Illinois and Indiana, as well as the Fisk and Crawford plants in Chicago–the need for coal and accompanying storage facilties in which to keep it has dropped dramaticaly.

But in an almost perverse turn of events, the controversial BP Whiting, Indiana refinery is about to finish a $3.8 billion expansion, which will make it the world’s second largest coker, which will process Canadian tar sands at an astounding rate. One of the by-products of that industry is something called petroleum coke or “petcoke.” According to Henry Henderson at the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC),
BP Whiting is now the second biggest producer of petcoke amongst American refineries. They will be spitting out 6,000 tons of the stuff a day ; more than 2 million tons annually.
Unfortunately, petcoke has a nasty habit of becoming wind-borne and ending up on people’s counter tops, windsills and in their eyes and lungs. And BP is now moving vast amounts of this substance across the state line to Chicago to holding areas on the banks of the Calumet River. Why? Because the environmental regulations aren’t as strict here. Which is ironic, considering that just last year BP agreed to a $400 million settlement with state and federal agencies as well as environmental and community groups over air quality standards around the Whiting facility.
At least this time, the threat to Chicago’s southeast side is being reported by some of the local media, including the Chicago Tribune and Chicago Tonight on WTTW. After being alerted by SETF, NRDC produced its own video of the rising piles of petcoke along the Calumet.
And Chicago isn’t even the first city to deal with this particular issue. Earlier this year, citizens of Detroit were alerted to similar clouds of black soot wafting over communities along the Detroit River. After public outrage from neighborhood groups and online entities like Sw Detroit Marathon Exposed and DCATS – Detroit Coalition Against Tar Sands, Detroit Mayor Dave Bing ordered the piles removed.
But where did the stuff end up? Nobody seems to know.
That’s where the headline at the top of this story comes from. The SETF’s Tom Shepherd says that he has asked the companies storing the petcoke in Chicago exactly where it came from and how it got there so quickly. But he has not received a straight answer. Is it possible that Chicago is now storing the petcoke that was ordered out of Detroit?
How are these two cases similar and how do they differ? According to a story on Climate Progress,
Detroit’s pet coke piles were produced by Marathon Refinery but owned by Koch Carbon, a subsidiary of Koch Industries. In Chicago they are owned by KCBX, an affiliate of Koch Carbon, which has large parcels of land along the Calumet River and, according to Midwest Energy News, expanded its presence in the area last year.
As you can see, the common denominator is Koch Industries. From an article on Daily Kos:
Because it’s a waste product of oil refining the Kochs sell it for prices cheaper than coal to poor nations willing the accept pollution as a trade off for cheap energy. Petcoke is the carbon cost ignored in the State department analysis that falsely claimed that Keystone XL tar sands oil will not significantly increase greenhouse gas pollution compared with conventional oil.

Which leads some people to refer to the substance as “petkoch.” The other connections, as noted above, are issues like the transportation of tar sands oil, the Keystone XL Pipeline, and recent tar sands oil spills like the one near Kalamazoo, Michigan, in 2010. Three years later, tar balls can still be found along the banks of that river, and dozens of families have been permanently displace.
That led to an action by the Michiana Coalition Against Tar Sands (MICATS) in September. As reported, interestingly, in the eNews Park Forest, they
set up a blockade of Enbridge Inc.’s expansion of tar sands pipeline 6b. This pipe- the same that ruptured in 2010 causing the largest and costliest inland oil spill in history- is currently under construction to increase the flow of tar sands from 240,000 barrels per day to 500,000 barrels per day.
It never ends, does it.
To address this very serious environmental issue, I’m pleased to have Tom Shepherd from SETF in studio. Joining us via phone are Chris Wahmhoff of Michigan Coalition Against Tar Sands (MI CATS) and Stephen Boyle from DCATS. By the way, Boyle points out that the Calumet River is currently the subject of remediation efforts by the U.S. EPA:
The 1.8-mile stretch of the river from Indianapolis Boulevard to Hohman Avenue is currently undergoing projects designed to remove contaminants and restore habitat. 350,000 cubic yards of sediment are slated to be removed and a cap will be placed over the dredged sediment. Wetlands and nearshore habitats will be restored with native plants following the completion of the dredging, expected in 2016.
Gosh, I can’t imagine that tons and tons of petcoke could possible affect that planned restoration.
Source: Mike Nowak, “This Week’s Show” (27 Oct 2013)